1System Architecture Overview
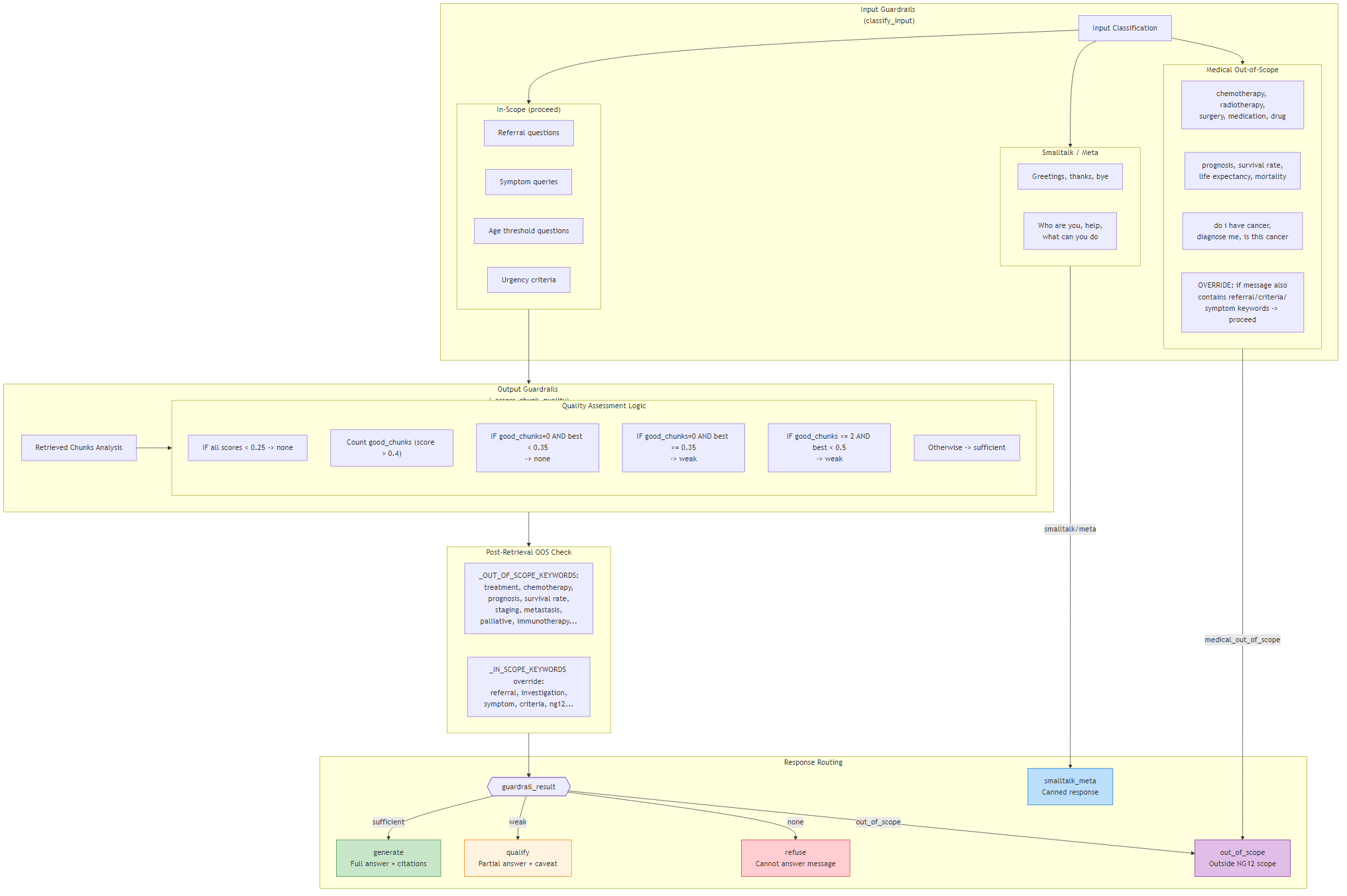
The system is organised into five layers: a single-page frontend, a FastAPI routing layer, LangGraph workflow agents, a shared RAG core, and external AI services.
The Frontend (index.html) provides three tabs —
Patient Assessment, Chat, and Vector DB Admin — each backed by a dedicated API router:
/assess/*, /chat/*, and /admin/*.
Routers delegate execution to two LangGraph workflow agents:
the Assessment workflow (4 nodes, structured clinical risk assessment for a specific patient)
and the Chat workflow (12 nodes, multi-turn Q&A with guardrails, query rewriting, and topic tracking).
Both workflows share a common core layer while differing only in reranking strategy inside the RAG pipeline.
Core modules include rag_pipeline.py (vector retrieval, mode-specific deterministic reranking, canonical resolution),
vector_store.py (ChromaDB wrapper), query_builder.py (A+C+B tiered query construction),
embeddings.py (Vertex AI client), and gemini_client.py (Gemini 2.0 Flash client).
Vector storage uses two logical layers in ChromaDB.
ng12_canonical holds verbatim guideline text — never embedded, accessed only by ID for citation and grounding.
ng12_guidelines holds the search-optimised chunks used for retrieval, mixing two document types:
rule_search (embedding-optimised rule representations, each referencing a single canonical via rule_id)
and symptom_index (Part B symptom table rows, each referencing one or more canonicals via references_json).
- Frontend: Single HTML page with 3 tabs + Architecture, Gallery, Notes, Readme pages
- Backend: FastAPI with 3 routers → 2 LangGraph workflow agents
- Shared Core: RAG pipeline (mode-aware reranking), vector store, query builder, embeddings, Gemini client
- Storage: ChromaDB (
ng12_canonicalfor citation,ng12_guidelinesfor retrieval), SessionStore (in-memory), patients.json - External: Vertex AI
text-embedding-004, Gemini 2.0 Flash
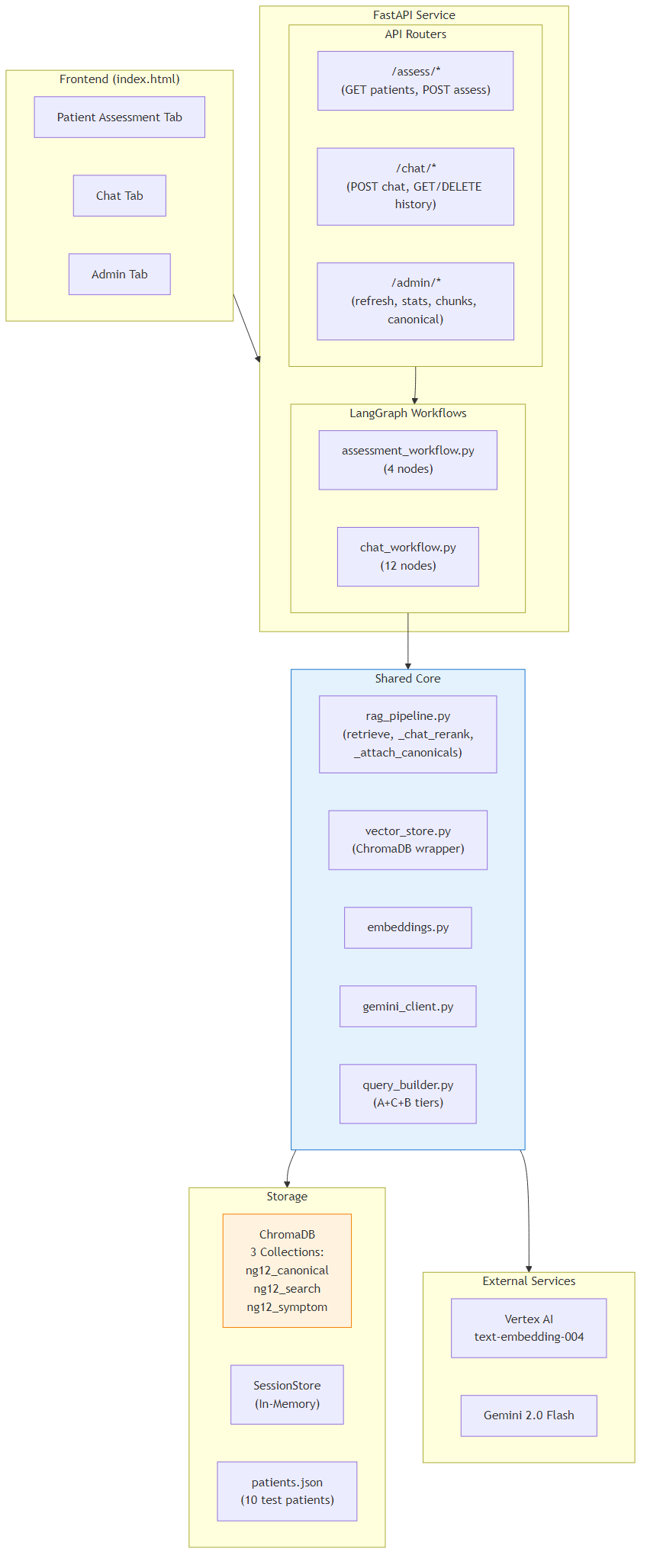
2PDF Ingestion Pipeline
Transforms the 85+ page NG12 PDF into structured, searchable chunks stored across three ChromaDB collections. A state-machine parser drives through three document regions: PART_A (clinical recommendations, pages 8-36), PART_B (symptom-to-cancer index tables, pages 37-82), and STOP (appendices, discarded).
Part A rules are detected via regex patterns matching section numbers (1.x.y) and recommendation verbs (Refer, Offer, Consider). Each rule is split into two companion chunks: a rule_canonical (verbatim PDF text for citation display) and a rule_search (template-enriched text with synonym expansion for better vector retrieval). Part B symptom tables produce symptom_index chunks with cross-references back to Part A rules.
- rule_canonical →
ng12_canonicalcollection (ID-based lookup, no embeddings) - rule_search →
ng12_guidelinescollection (vector similarity search) - symptom_index →
ng12_guidelinescollection (vector similarity search) - Metadata extracted: section, cancer_type, action_type, age thresholds, symptom keywords, urgency, gender, risk factors
- Embeddings generated via Vertex AI
text-embedding-004
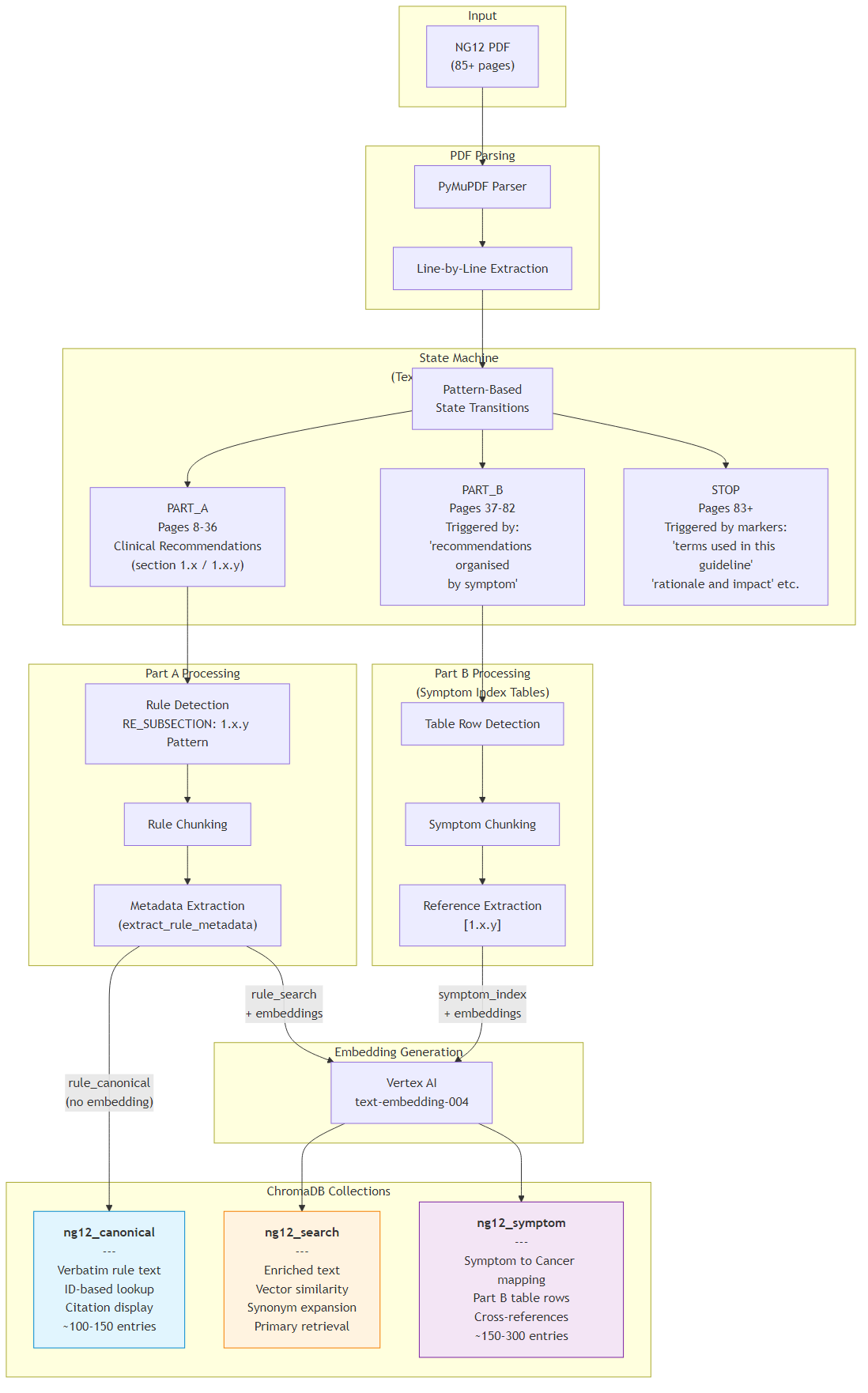
3Patient Assessment Workflow
A LangGraph workflow that performs clinical risk assessment against NG12 guidelines. Given a patient ID, the system fetches patient data (age, symptoms, smoking history, gender), retrieves relevant guideline chunks via the RAG pipeline with patient-specific reranking, then asks Gemini 2.0 Flash to assess cancer risk and produce a structured JSON response.
The fetch_patient node first attempts Gemini function calling (tool use) to look up patient data;
if credentials are unavailable, it falls back to a direct database lookup from patients.json.
The retrieve_guidelines node constructs a query string from the patient's symptoms, age, gender, and smoking history,
then calls rag_pipeline.retrieve(top_k=8, patient_data=patient) which applies deterministic scoring boosts for age, symptom overlap, smoking, and gender matching.
The assess_risk node sends the patient data and retrieved chunks to Gemini with a strict JSON-only system prompt,
producing risk_level, cancer_type, recommended_action, reasoning, and matched_recommendations.
- 3 LangGraph nodes: fetch_patient → retrieve_guidelines → assess_risk (+ handle_error)
- Patient scoring boosts: +0.15 age match, +0.10 symptom overlap, +0.10 smoking, +0.05/-0.30 gender
- Output: risk_level, cancer_type, recommended_action, reasoning, matched NG12 recommendations with citations
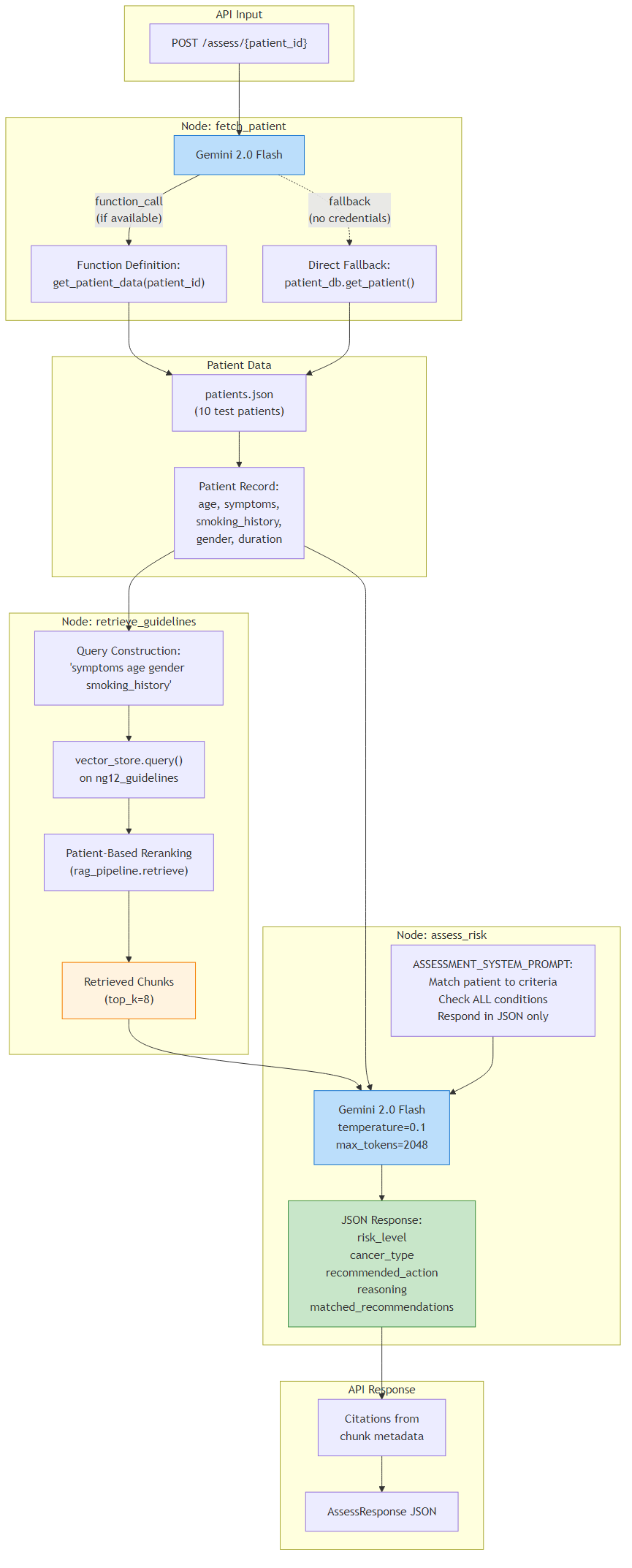
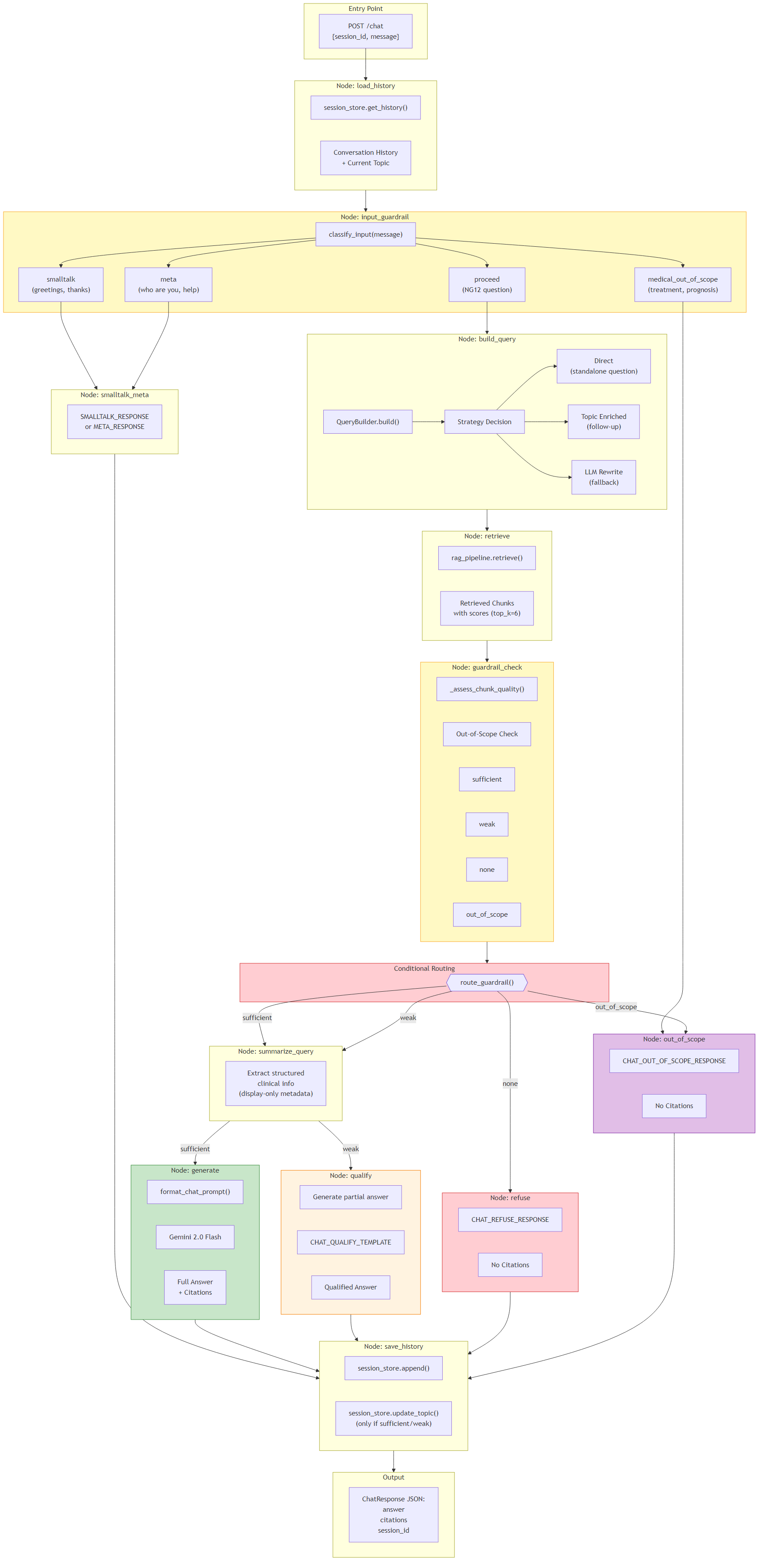
4Chat Workflow (LangGraph)
A 12-node LangGraph workflow powering multi-turn conversational Q&A about NG12 guidelines. Features a dual-guardrail system: an input guardrail classifies messages into smalltalk, meta, medical_out_of_scope, or proceed; and an output guardrail assesses retrieved chunk quality to route between four response paths.
The input guardrail short-circuits non-clinical queries (greetings, "who are you", treatment/prognosis questions) with canned responses, avoiding unnecessary RAG retrieval. For in-scope questions, the system builds a search query using the A+C+B tiered strategy, retrieves chunks, then the output guardrail evaluates chunk quality scores to determine the response path: generate (sufficient evidence — full grounded answer with citations), qualify (weak evidence — hedged partial answer), refuse (no evidence — suggests reformulating), or out_of_scope (detected non-NG12 topic).
- Flow: load_history → input_guardrail → build_query → retrieve → guardrail_check → summarize_query → generate/qualify/refuse/out_of_scope → save_history
- Session tracking: conversation history + topic extraction from cited chunks for context-aware follow-ups
- Query summary: Gemini extracts structured clinical info (symptoms, age, duration) for display transparency
- Topic updates only on sufficient/weak results with valid citations
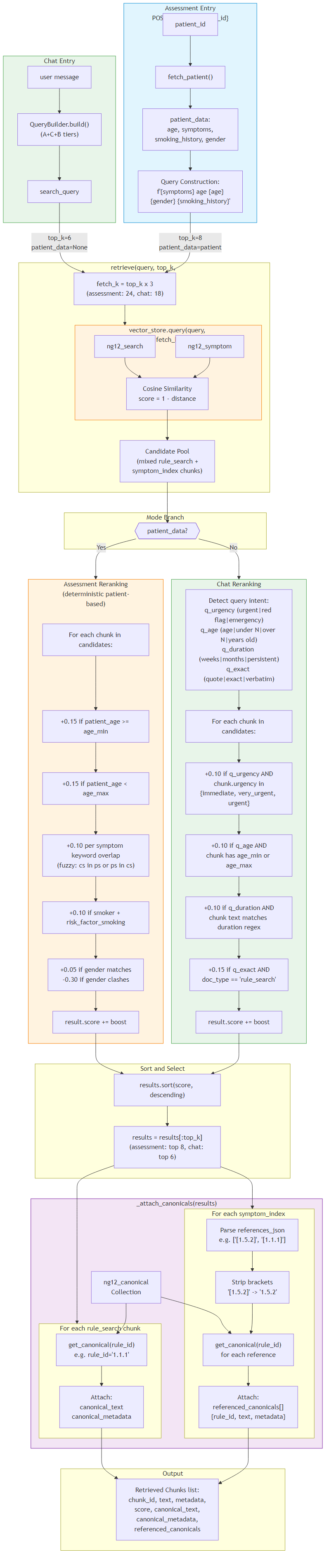
5Retrieval Pipeline (Detailed)
A shared retrieval engine used by both the Assessment and Chat workflows.
It queries ChromaDB's ng12_guidelines collection for a 3× candidate pool
(fetch_k = top_k * 3) using cosine similarity, then applies mode-specific additive reranking
and re-sorts by the adjusted score before returning the final top_k results.
Assessment mode (patient_data provided): deterministic clinical boosts are applied (age threshold matches, symptom keyword overlap, smoking risk factor, and gender match/clash).
Chat mode (patient_data absent): lightweight intent boosts are applied based on query signals (urgency, age mentions, duration intent + duration terms present in chunk text, and exact-wording requests favouring rule_search).
After reranking, results are enriched via _attach_canonicals() by resolving evidence from the canonical store through ID lookup:
- rule_search → attaches a single canonical rule (
canonical_text,canonical_metadata) viarule_id - symptom_index → attaches multiple referenced canonicals (
referenced_canonicals) viareferences_json
The enriched chunks are then passed into the downstream LLM prompt in both workflows.
6-Step Flow
- Query enters RAG pipeline → vector search against
ng12_guidelines(rule_search + symptom_index mixed) - Candidate recall →
fetch_k = top_k × 3chunks via cosine similarity - Mode-specific reranking → Assessment: patient-driven clinical boosts | Chat: query-intent-driven boosts
- Score adjustment & sorting →
final_score = base_similarity + additive boosts, re-sort candidates - Canonical resolution → rule_search: resolve
rule_id→ single canonical | symptom_index: resolvereferences_json→ multiple canonicals - LLM grounding → enriched chunks (including symptom_index + resolved canonicals) are passed directly into the LLM prompt
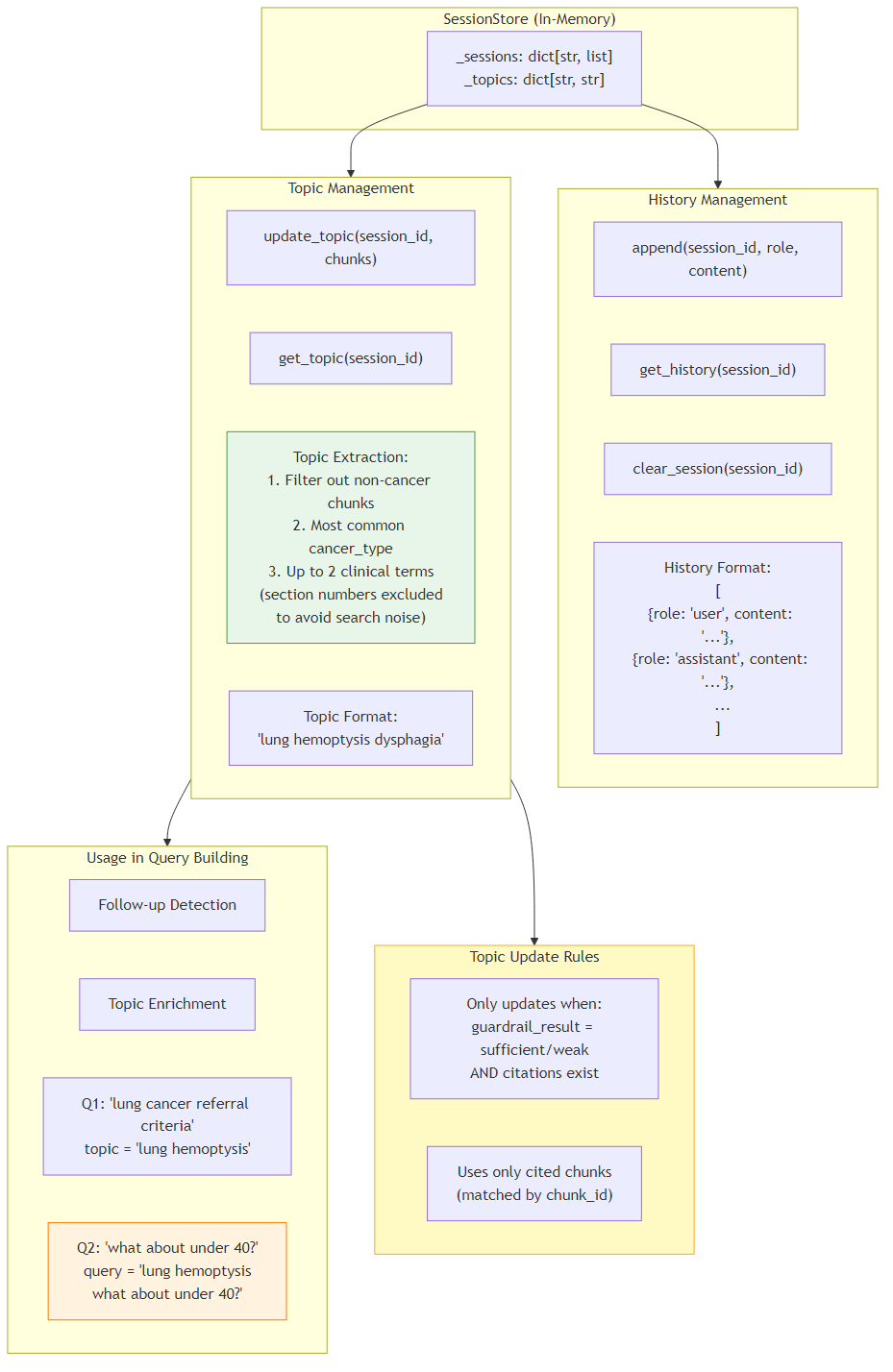
6Memory & Topic Management
The in-memory SessionStore manages conversation history and topic tracking for multi-turn chat sessions. Each session maintains a list of user/assistant message pairs and a dynamically extracted topic string that captures the clinical context of the conversation.
Topic extraction works by analyzing the chunks that were actually cited in the response: it identifies the most common cancer_type and up to 2 clinical terms (section numbers are excluded to avoid search noise). Topics are only updated when the guardrail result is "sufficient" or "weak" and valid citations exist, ensuring the topic reflects genuinely relevant content. The topic is then used by the QueryBuilder's Tier C (topic_enriched) strategy to enrich follow-up queries (e.g., if topic is "lung hemoptysis" and user asks "what about under 40?", the search query becomes "lung hemoptysis what about under 40?").
- History: append(session_id, role, content) / get_history(session_id) / clear_session(session_id)
- Topic: update_topic(session_id, chunks) / get_topic(session_id)
- Topic format: space-separated keywords like "lung hemoptysis dysphagia"
- Update rule: only from cited chunks when guardrail_result is sufficient/weak
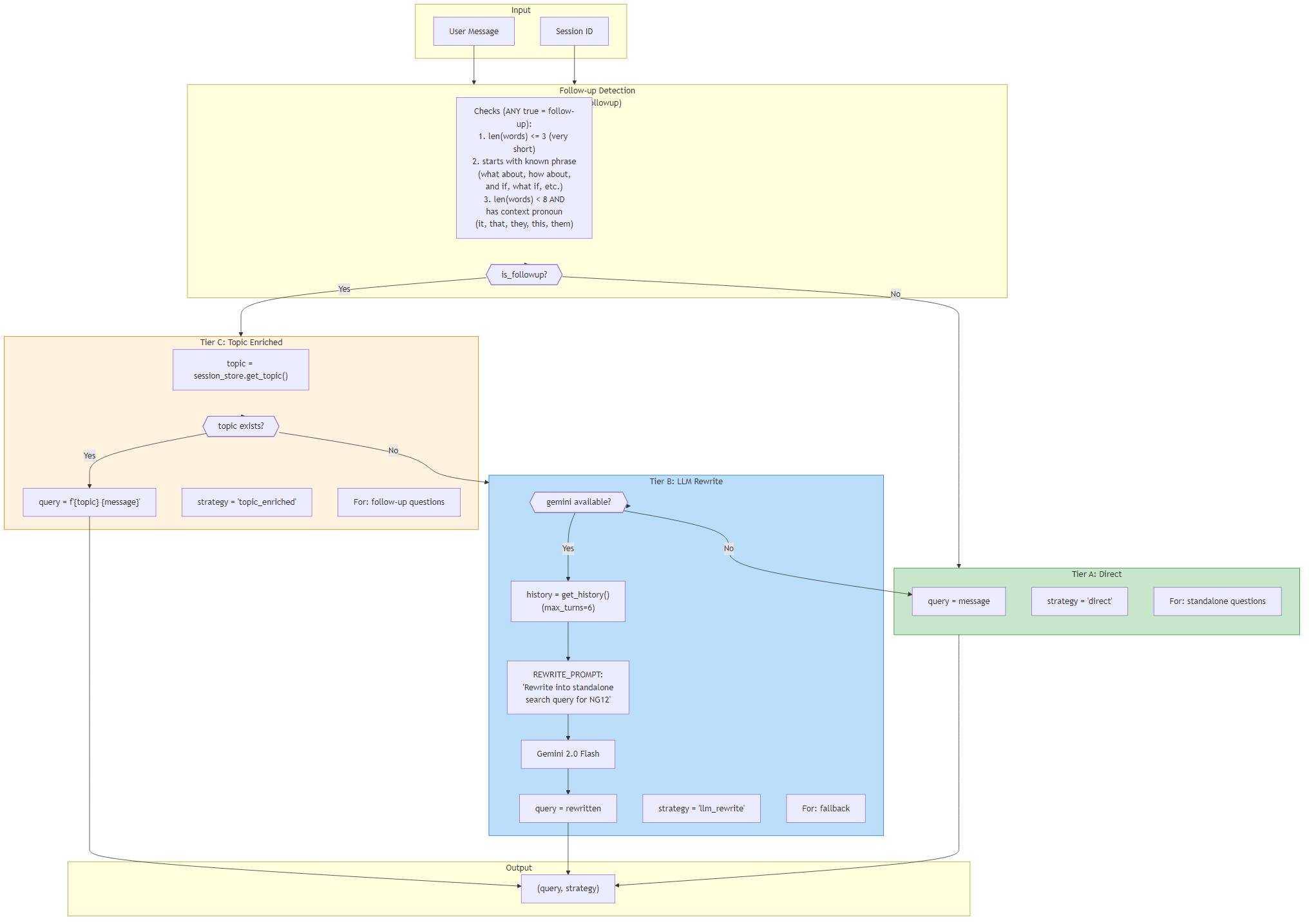
7Query Builder Strategy (A+C+B Tiers)
The QueryBuilder uses a tiered fallback strategy to construct optimal search queries for the RAG pipeline. It first detects whether the user's message is a follow-up question, then selects the appropriate query construction approach.
Follow-up detection uses three heuristics: very short messages (≤3 words), messages starting with known phrases ("what about", "how about", "and if", "what if"), and short messages (<8 words) containing context pronouns (it, that, they, this, them). For standalone questions, Tier A (direct) passes the raw message as the search query. For follow-ups with an existing session topic, Tier C (topic_enriched) prepends the topic to provide context. If no topic exists, Tier B (llm_rewrite) uses Gemini to rewrite the follow-up into a standalone search query using conversation history (max 6 turns). If Gemini is unavailable, it falls back to Tier A.
- Tier A: Direct — raw message as query (standalone questions)
- Tier C: Topic Enriched — "{topic} {message}" (follow-ups with topic)
- Tier B: LLM Rewrite — Gemini rewrites to standalone query (follow-ups without topic)
- Follow-up markers: short length, starter phrases, context pronouns
8Query Rewriting / Summarization
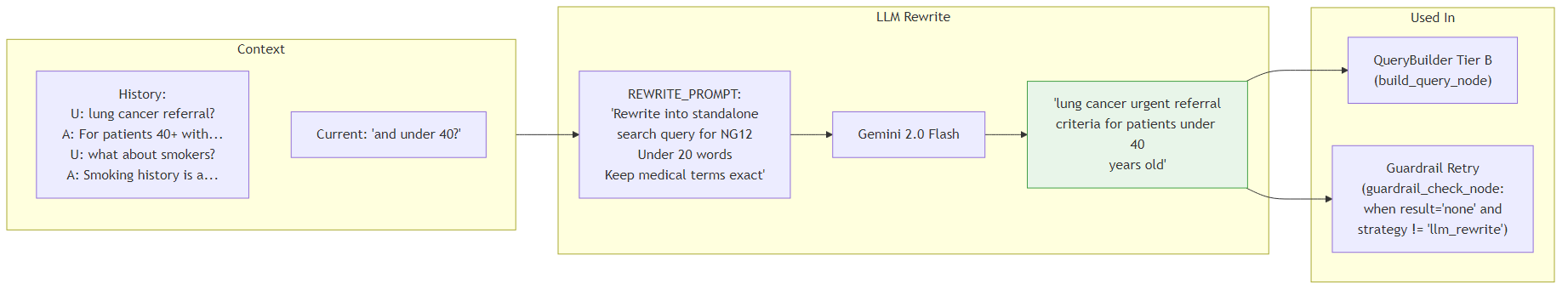
When a follow-up question cannot be enriched with a session topic (Tier B fallback), the system uses Gemini 2.0 Flash to rewrite the ambiguous follow-up into a standalone search query using the conversation history as context.
The REWRITE_PROMPT instructs Gemini to produce a query under 20 words while keeping medical terms exact. For example, given a history discussing lung cancer referral criteria and a follow-up "and under 40?", the LLM produces: "lung cancer urgent referral criteria for patients under 40 years old". This rewriting is also triggered as a retry mechanism in the guardrail_check node: if the initial retrieval returns no relevant chunks (result='none') and the current strategy isn't already 'llm_rewrite', the system rewrites the query and retries retrieval once before giving up.
- Used in: QueryBuilder Tier B (build_query_node) and guardrail_check retry
- Input: conversation history (max 6 turns) + current message
- Output: standalone search query under 20 words
- Medical terms preserved exactly as written (no paraphrasing clinical terminology)
9Input / Output Guardrails
A dual-layer guardrail system that prevents hallucination and keeps responses within NG12 scope. The input guardrail (classify_input) uses regex/keyword matching (no LLM call) to classify messages into four categories: smalltalk, meta, medical_out_of_scope, or proceed.
The output guardrail (_assess_chunk_quality) analyzes retrieved chunk scores to determine evidence quality. If all scores < 0.25, it returns "none". It counts good_chunks (score > 0.4): zero good chunks with best < 0.35 yields "none"; with best ≥ 0.35 yields "weak"; ≤2 good chunks with best < 0.5 yields "weak"; otherwise "sufficient". A post-retrieval out-of-scope check compares the query against treatment/prognosis keywords (with override if referral/symptom keywords are also present). Each guardrail result maps to a dedicated response path with appropriate templates: full answer (sufficient), hedged answer (weak), refusal (none), or scope message (out_of_scope).
- Input categories: smalltalk, meta, medical_out_of_scope, proceed
- Output thresholds: none (<0.25 or no good chunks), weak (borderline), sufficient (strong evidence)
- 5 response paths: generate, qualify, refuse, out_of_scope, smalltalk_meta
- Medical OOS override: if message also contains referral/criteria/symptom keywords → proceed anyway